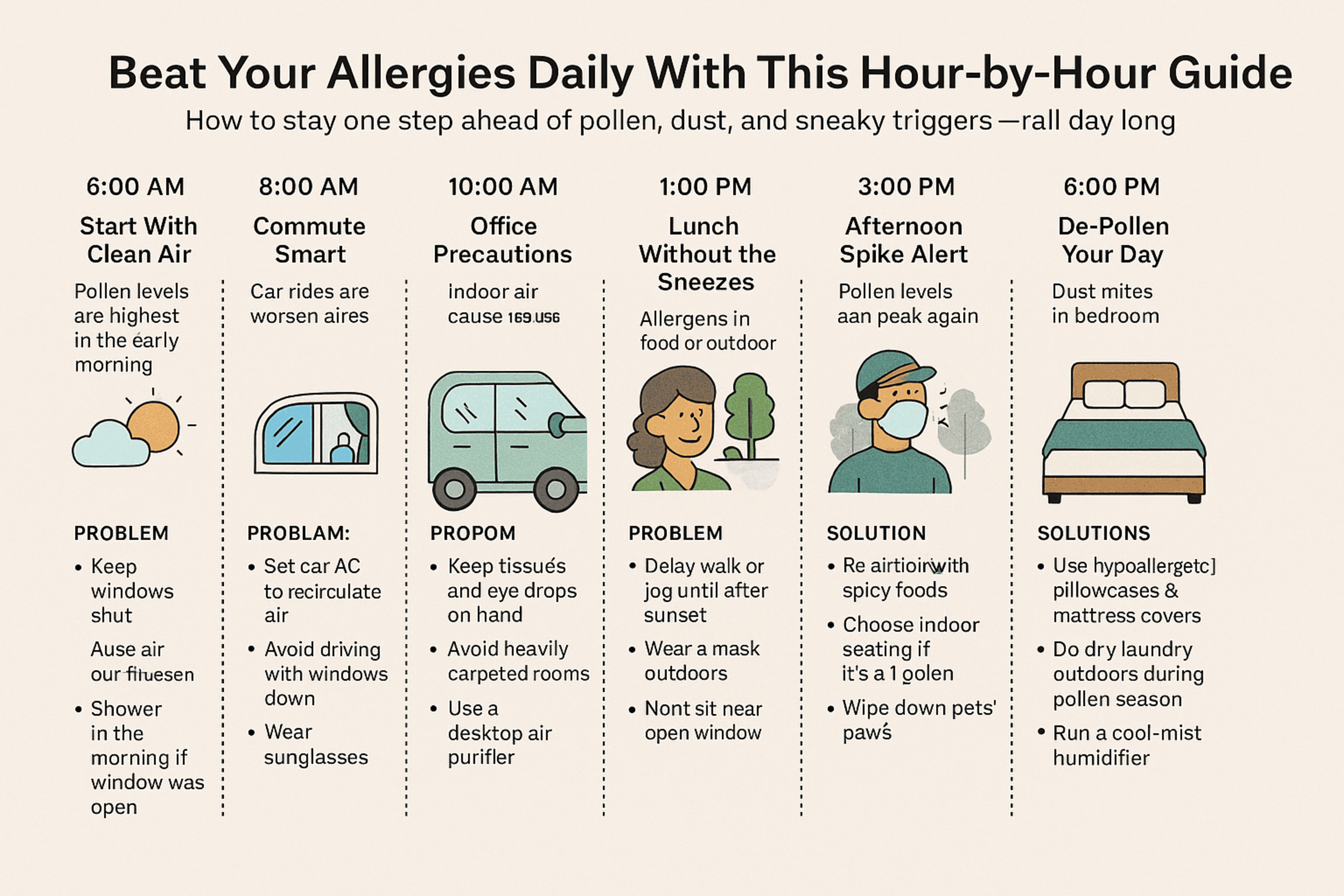
When we hear the word “diabetes,” we often picture one condition — but did you know there are actually several different types of diabetes, and each works a little differently?
Let’s break them down in a way that’s easy to understand — because whether it’s affecting you or someone you love, knowledge is power when it comes to managing diabetes.
🌟 So, What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy — specifically how it uses glucose (sugar) and insulin.
- When we eat, our body breaks food into glucose, which enters our bloodstream.
- In response, the pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps glucose get into our cells for energy.
- If your body doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use it properly, glucose builds up in the blood — leading to high blood sugar levels.
That’s where diabetes comes in.
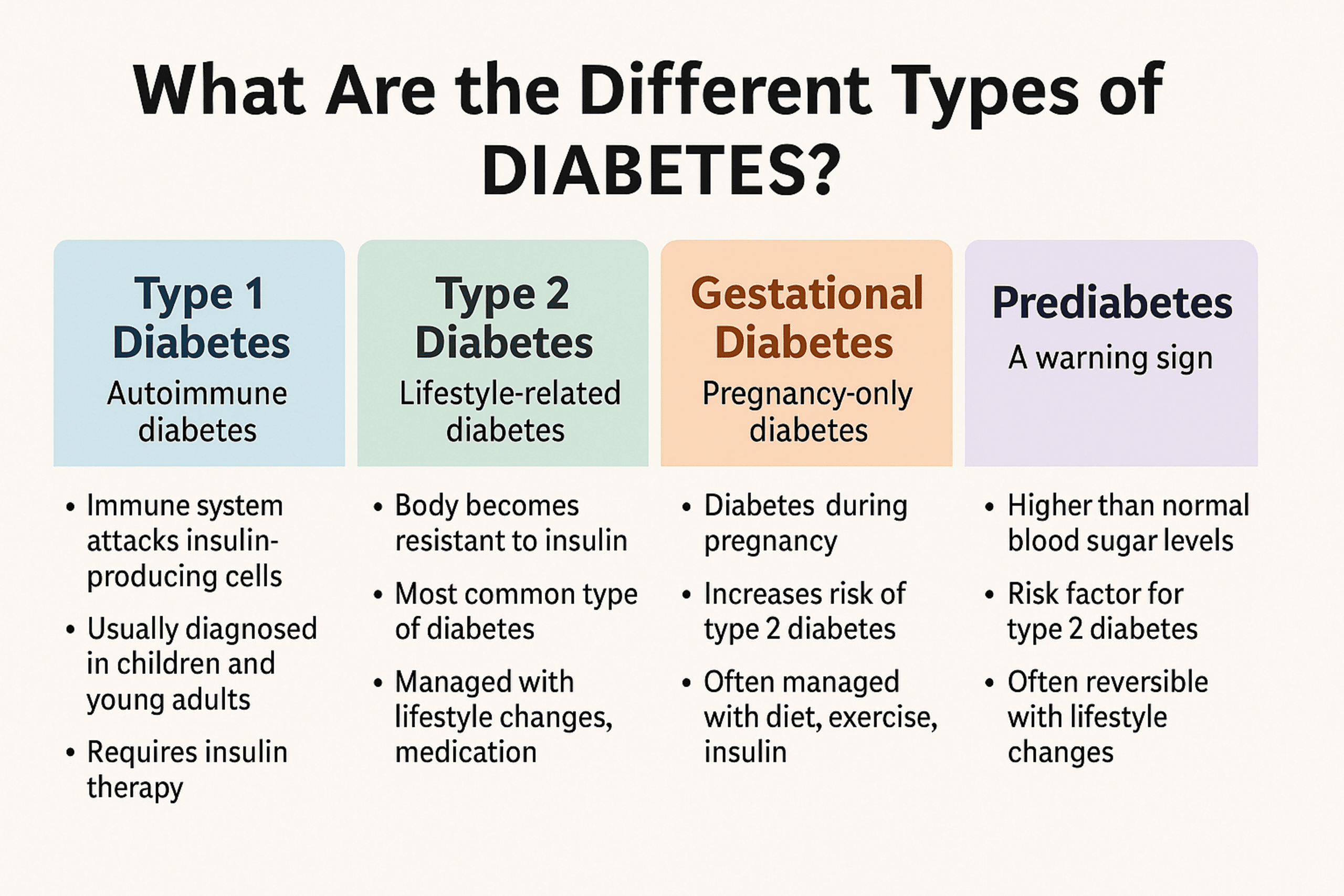
🧬 1. Type 1 Diabetes — “Autoimmune Diabetes”
What happens:
The immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Key facts:
- Usually diagnosed in children or young adults, but can occur at any age.
- The body makes little to no insulin.
- Daily insulin injections or a pump are required to survive.
🧠 Think of Type 1 like a locked door — without insulin, the sugar can’t get inside your cells.
🍞 2. Type 2 Diabetes — “Lifestyle-Related Diabetes”
What happens:
The body becomes resistant to insulin, or the pancreas doesn’t produce enough.
Key facts:
- Most common type — about 90–95% of all diabetes cases.
- Linked to genetics, weight, inactivity, and age (usually adults, but now seen in teens too).
- Managed with lifestyle changes, oral meds, and sometimes insulin.
💡 The body has insulin, but it’s like a broken key — it doesn’t work well enough.
🤰 3. Gestational Diabetes — “Pregnancy-Only Diabetes”
What happens:
Hormones from the placenta make the mother’s body insulin-resistant.
Key facts:
- Occurs only during pregnancy, often in the 2nd or 3rd trimester.
- Usually goes away after birth — but increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later.
- Managed through diet, exercise, and sometimes insulin.
👶 Regular screening during pregnancy is vital for catching this early.
🧪 4. Prediabetes — “A Warning Sign”
What happens:
Blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis.
Key facts:
- Affects 1 in 3 adults, often without symptoms.
- Can be reversed with healthy eating, exercise, and weight loss.
- Without action, it often turns into Type 2 diabetes.
🚨 It’s your body’s way of waving a red flag. The good news? You can turn it around.
🧬 5. Other Rare Types — Genetic or Secondary Diabetes
There are some rare forms of diabetes, such as:
- MODY (Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young): A genetic form seen in young people.
- LADA (Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults): Similar to Type 1 but slower to develop.
- Secondary diabetes: Caused by other conditions (like pancreatitis) or medications (like steroids).
👩⚕️ Final Thoughts: Know Your Type, Know Your Plan
Every type of diabetes is different — but all of them can be managed with the right care, information, and support.
If you or someone you know is showing symptoms like:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
👉 Don’t guess — talk to a doctor and get tested.
Because early detection can save lives — and change them.